They’re on restaurant menus, concert tickets, parcel boxes, even the side of your cereal packet. But have you ever stopped to wonder—how do QR codes work?
These pixelated little squares are now a gateway to information, experiences, and transactions, all with a single scan. In this guide, we’ll break down the mystery behind them, from the anatomy of a QR code to how your phone instantly transforms it into a link, message, or app. Whether you’re a tech novice or a curious consumer, we’ve got you covered.
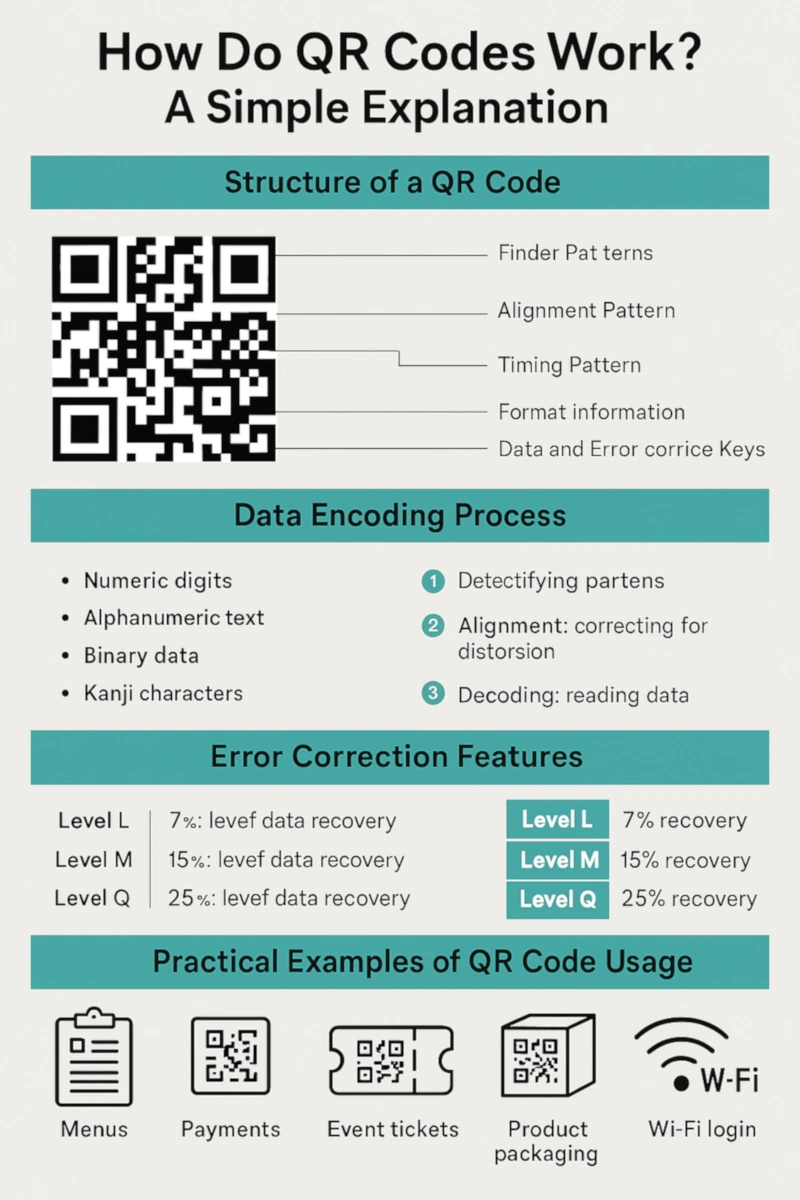
QR Code Structure: A Pixelated Powerhouse
A QR code—short for “Quick Response” code—is a two-dimensional barcode consisting of black squares arranged on a white background. Unlike traditional barcodes that carry information in one direction (horizontally), QR codes store data both horizontally and vertically. This allows them to pack in much more information.
Each QR code contains the following key elements:
– Finder Patterns
– Alignment Pattern
– Timing Pattern
– Format Information
– Data and Error Correction Keys
This clever design is what makes QR code scanning fast and reliable—even if part of the code is scratched or obscured.
The Data Encoding Process: More Than Meets the Eye
The secret sauce behind how QR codes work lies in the data encoding process. QR codes can contain numeric digits, alphanumeric text, binary data, and Kanji characters.
When a message is converted into a QR code, it’s first broken down into smaller chunks. Each piece is then encoded using patterns of black and white squares. A QR code can store up to 7,089 numeric characters or 2,953 bytes, depending on its version.
QR Code Scanning: What Happens Behind the Scenes?
Here’s where the magic happens. When you point your smartphone camera at a QR code:
1. Detection
2. Alignment
3. Decoding
This whole process takes less than a second.
QR Code Error Correction: The Lifesaver Feature
QR codes are designed with error correction. Thanks to Reed-Solomon error correction, they can withstand:
– Level L: 7% data recovery
– Level M: 15%
– Level Q: 25%
– Level H: 30%
This means a QR code can still work even if nearly a third of it is missing.
Real-World QR Code Examples That Just Make Sense
Some standout QR code examples include:
1. Restaurants and Cafés
2. Payments
3. Event Tickets
4. Product Packaging
5. Supply Chain Management
6. Wi-Fi Login
Why QR Codes Are Here to Stay
QR code structure allows more data and faster access than traditional barcodes. QR code scanning only needs a smartphone. QR code error correction ensures it works even when damaged.
Final Thoughts
From understanding the QR code structure and data encoding process to decoding and error correction, you now know exactly how QR codes work—and why they’re transforming how we interact with the world around us.
